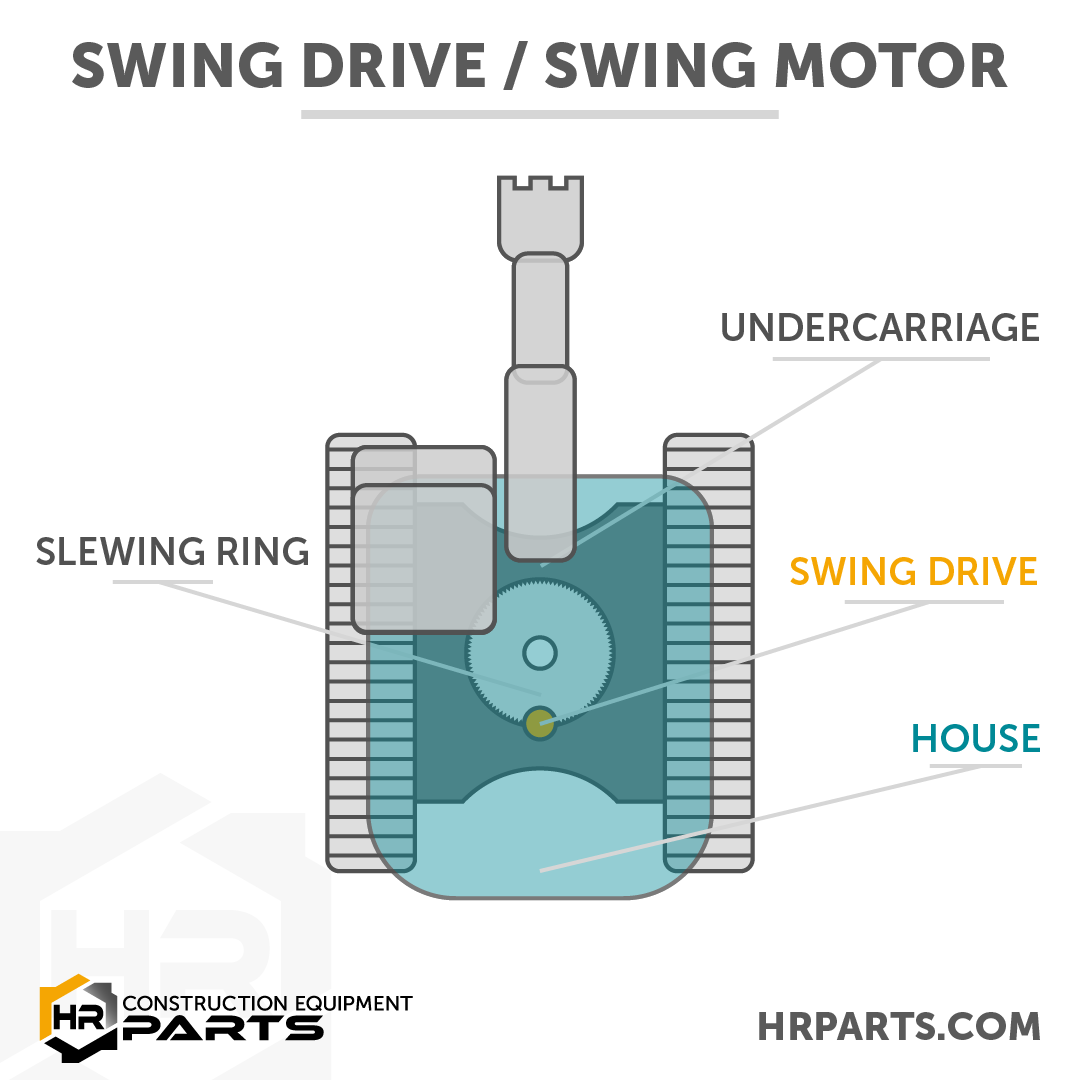
What is a Swing Drive with Swing Drive Diagram
An excavator is a versatile and important machine in the construction industry and today with new, smart tools and job-specific attachments the range of work excavators perform continues to grow. But no matter how the excavator evolves, many of its core parts remain the same -- final drives and travel motors to propel and position the excavator; cylinders to control the stick and boom; tracks or wheels, springs and sprockets, valves and buckets; and at its core a swing drive to allow the machine to eloquently and easily pivot and spin its house and attachments.
In fact, the ability to swing is one of the main properties that separates the excavator from other digging machines. If you’ve ever wondered exactly what the swing drive is and how it works, this is the article for you.
What is a swing drive on an excavator?
- A swing drive is a hydraulically-driven component on an excavator and most swing drives consist of a hydraulically-powered swing motor attached to a swing gear box that consists of at least one, but more often multiple sets of planetary gears.
- The planetary gears on a swing drive are designed to convert rotational force into torque and to output that force through a pinion gear which extends from the bottom of the swing drive.
- A swing drive connects the upper components and lower components of an excavator at a pinion gear which interacts with a large, stationary gear known by multiple names, including: slewing gear, slewing bearing, ring gear, ring bearing, or turntable bearing.
Where on an excavator is a swing drive located?
- A swing drive sits at the center of an excavator and divides the upper, pivoting, parts of an excavator from the lower, traveling, parts of an excavator. The swing drive allows the upper components of the machine to rotate 360 degrees around its center axis.
- Without a swing drive the excavator’s house and attachments would be fixed and stationary in relation to its tracks and an operator would have to reposition the entire machine to alter the position of the excavator’s digging tools -- greatly reducing the excavator’s unique benefit to a worksite.

How does a swing drive work?
- The end effect of the swing drive is (simply put) to allow the upper components of the excavator to swing, but the overall design must also ensure the swinging motion is smooth, operates under defined guidelines, and is able to be finely controlled by a well-trained operator.
- The internal hydraulic components and design of swing drives implement a number of valves, ports, and bearings to allow an operator to control the speed and direction of the motor while also including safety measures to prevent damage to the machine. Since both the machine’s components being moved are robust and a load is often added on, the swing motor must be designed to control for changes in momentum, operating on uneven ground, and consistent high-impact connections between parts.
- By opening and closing hydraulic ports inside the swing drive (through a joystick in the cab) the operator is able to control the speed and direction of internal components and, in turn, the movement and position of all the upper parts of the excavator.
- At the bottom of a swing gear the teeth of a pinion gear connect to the teeth of a slewing gear in the excavators carbody -- as the pinion gear rotates the upper components of the excavator revolve around the inside of the static slewing gear.
How do you operate a swing drive?
- Because of the unique design of excavators, the controls inside of the cab of an excavator are as detailed and complex as any video game you’d find in your living room. The swing drive introduces a new axis of control to the machine and with it, an additional input system. In the cab of the machine, there are pedals and handles to control the undercarriage and two joysticks to control the boom, stick, bucket, and swing of the machine -- along with a slew of smart controls, screens, and tech-forward widgets.
- An expert excavator operator can combine the actions of all the excavator’s component parts to perform intricate and detailed movements and expertly interact with their external environment. In skilled hands the swinging mechanism of the excavator helps to make swift and precise work of a wide range of jobs.
What are the parts of a swing drive?
Swing Motor
The upper part of the swing drive is a hydraulic swing motor that consists of a number of valves, ports, and bearings that control how and when hydraulic fluid flows and powers the attached gearbox. Safety mechanisms inside the motor must account for feedback from the machine and be designed to work under intense pressure.
Swing Gearbox
The swing gearbox consists of a number of planetary gear systems, each designed to convert energy from high speed input into lower speed, high torque output. High torque power is necessary to swing the weight of the house, along with any load, and ensure movement is fluid and the machine performs properly on the job.
Planetary Gear System
A planetary gear system consists of multiple planet gears orbiting a central sun gear. Through gear reduction power is transferred into high torque output.
Pinion Gear Shaft
The pinion gear shaft extends from the bottom of the swing drive and interacts directly with the slewing gear in the carbody of the excavator. The interaction of the teeth on the pinion and the teeth in the slewing gear rotates the swing motor and, in turn, swings the excavator’s house.
Slewing Gear / Slewing Ring
While not a part of the swing drive, the slewing gear is the component attached to the excavator’s undercarriage that contains the swing drive, directs its path, and facilitates its swinging of the house.
Learn more about planetary gears and torque in our What is a Final Drive article.
While there’s certainly quite a bit of complexity still to cover on a swing drive and an excavator, hopefully this short article has helped reveal the basics of a swing drive and its functions. If you’re looking for more information, check out a swing drive disassembly from the experts in our Recon and Rebuild shops to see right inside a swing drive.
And, as always, if you’re searching for a swing drive, a swing motor, a slewing gear, or any parts for your excavator, our H&R parts specialists are always here to help with fast access to the parts you need and expert advice to get you back up and running.
Swing Drive Image Gallery